By 2026, AI is no longer confined to a single execution environment. The rapid evolution of hardware, advances in model optimization, and the growing availability of AI‑native chips in enterprise endpoints have dramatically expanded where intelligence can live and operate. At the same time, cloud AI continues to advance at a remarkable pace, offering access to the largest models, the richest context windows, and the most sophisticated reasoning capabilities.
This divergence has placed enterprises at strategic crossroads. Leaders must now weigh how to deliver fast, private, cost‑effective AI experiences while still benefiting from the scale and innovation of cloud‑based intelligence. The choices ahead are no longer binary, and the architecture decisions enterprises make today will shape the performance, economics, and resilience of their AI systems for years to come.
Why is 2026 an Inflection Point for Enterprise AI Architecture?
Over the past three years, the AI landscape has transformed at a pace unprecedented even in the technology sector:
- On-device compute power has surged, with leading mobile and PC chipsets offering 30–60 TOPS of NPU performance—enough to run advanced language and vision models locally.
- Model compression, quantization, and distillation techniques have made it possible to run models that once required racks of GPUs directly on edge devices.
- Network constraints and compliance pressures have intensified, forcing enterprises to reconsider the feasibility of cloud-only approaches.
- Hybrid orchestration frameworks are maturing, enabling seamless distribution of inference loads between device and cloud.
Taken together, these trends mean enterprises are no longer forced into a binary choice. Instead, the question becomes: Which workloads belong where, and why?
The Cloud-Only AI Model: Strengths and Limitations
For over a decade, cloud infrastructure has been the dominant engine powering enterprise for AI. In the context of GenAI and large language models (LLMs), “cloud‑only” describes a model where all AI computation happens entirely in remote data centers. When a user interacts with popular systems like GPT‑4, Claude, or Gemini, their prompts, documents, images, or voice recordings are sent from the device to cloud servers equipped with advanced GPUs and AI accelerators. These servers run extremely large models—often with billions or even trillions of parameters—and return the generated response in real time.
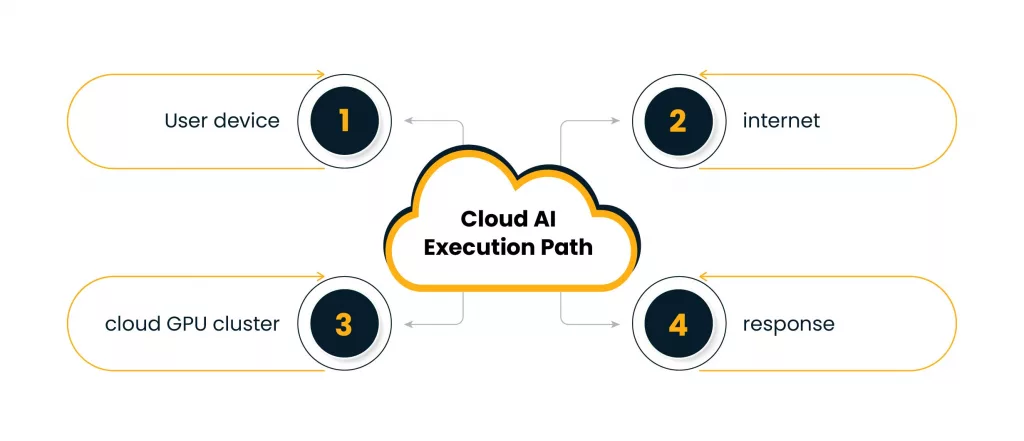
This architecture powers many everyday GenAI experiences. Chat-based assistants rely on cloud-scale reasoning; multimodal models process images and documents centrally, and enterprise copilots use vast context windows and shared organizational knowledge graphs. Cloud-only systems also enable high-impact workloads such as semantic search across enterprise data lakes, generative code completion, and large-scale image or video analysis used in insurance, retail, and healthcare. Examples recognizable in daily enterprise use include GPT-powered summarization tools, Claude-based document reasoning systems, and Gemini models supporting multimodal workflows.
Cloud-only AI became the default for early generations of GenAI because these models were simply too large and computationally demanding for endpoint devices. The cloud provided the scale, memory, and accelerator capacity required to run frontier models while allowing enterprises to adopt GenAI rapidly without investing in specialized hardware.
Strengths
- Unlimited scalability and elasticity
Cloud platforms excel in handling large model sizes, massive datasets, and unpredictable demand. Enterprises benefit from global availability zones, usage-based billing, and the ability to scale AI workloads in seconds.
- Access to the latest and most powerful models
Foundation model updates—often too large or complex for edge deployment—arrive first in the cloud. For use cases requiring high accuracy, multi-modal fusion, or extensive reasoning, cloud AI continues to lead.
- Centralized governance and monitoring
Model updates, policy enforcement, audit trails, and compliance workflows are most effective when managed from a centralized control plane.
Limitations
- Latency and reliability constraints
In industries where milliseconds matter—such as manufacturing automation, autonomous systems, financial trading, and healthcare diagnostics—cloud round trips can introduce delays that are operationally significant.
- Ongoing operational cost exposure
Pay-as-you-go inference models can scale costs rapidly. For high-volume, low-complexity inference workloads, cloud-only pricing may exceed the long-term total cost of ownership of on-device or hybrid approaches.
- Privacy, data locality, and regulatory barriers
Sensitive workloads increasingly face restrictions related to data residency, cross-border transfers, and industry-specific privacy and compliance requirements.
In short: cloud AI is powerful, but not universally optimal.
The Rise of On-Device AI: What Changed?
By 2026, running AI directly on devices—smartphones, PCs, IoT equipment, cars, industrial sensors—is no longer experimental. It’s production ready. In the context of GenAI and LLMs, on‑device models refer to optimized versions of language and multimodal models that can execute entirely on local hardware without relying on cloud data centers. This shift is powered by breakthroughs in quantisation techniques (such as 4‑bit and 8‑bit formats), efficient model packaging formats like GGUF, and lightweight runtimes such as Ollama and vLLM, which make it possible to deploy smaller yet highly capable models directly onto endpoints.
Examples of on‑device GenAI include running compact LLMs like Llama‑3‑instruct variants on a laptop or phone, using multimodal assistants that process images locally for privacy‑preserving workflows, or deploying summarisation and translation models that continue functioning even when offline. These capabilities allow enterprises to offer near‑instant AI responses, preserve sensitive data on the device, and reduce dependence on cloud‑based inference.
Key Catalysts
- NPUs with massive on-device acceleration
Modern NPUs deliver double- and triple-digit TOPS performance while maintaining energy efficiency suitable for continuous, real-time operation.
- Model optimization breakthroughs
Advances such as 4-bit quantization, LoRA adapters, pruning, and distillation enable high-performing models to operate within the memory and compute constraints of edge hardware.
- Offline and low-latency experiences
On-device AI enables instant responsiveness, even in air-gapped environments or locations with limited or unreliable connectivity.
Enterprise Advantages
- Speed: Latency drops from tens or hundreds of milliseconds to under 10ms for many workloads.
- Cost efficiency: Once deployed, inference is essentially free compared to cloud usage fees.
- Privacy & security: Data stays on the device; raw information doesn’t need to travel or persist outside the enterprise perimeter.
- Resilience: Systems continue functioning during outages or network degradation.
Challenges
- Model size limitations still matter; not all workloads fit edge constraints.
- Fleet management complexity increases when thousands or millions of devices require synchronized updates.
- Hardware variability introduces performance unpredictability.
On-device AI is momentum-rich, but not a universal replacement for cloud AI.
The Hybrid Model: The Strategic Architecture for Enterprises in 2026
A hybrid AI approach blends on‑device inference with cloud‑based intelligence—each doing what it does best. In the context of GenAI and LLMs, hybrid adoption has accelerated because major AI labs like Meta, DeepSeek, and Google now offer model families specifically designed to operate across both environments. Frontier‑scale models run in the cloud for deep reasoning and high‑context tasks, while smaller, optimized variants run locally to deliver instant responses, preserve privacy, and reduce cloud dependency.
Meta’s Llama ecosystem illustrates this shift clearly: cloud‑scale Llama models handle intensive workloads, while device‑ready versions such as Llama 1B, 3B, and 11B bring meaningful on‑device intelligence to laptops, phones, and embedded systems. DeepSeek’s R1 family follows the same pattern—its largest models excel in cloud environments, while compact formats like 1.5B, 7B, and 8B enable local inference for latency‑sensitive or offline use cases. Google’s model portfolio reinforces the trend with Gemma 3 supporting cloud‑scale applications and Gemma 3n engineered specifically for mobile and edge devices.
Together, these dual‑format model families give enterprises something they never had before: the ability to combine the raw intelligence of frontier models with the speed, autonomy, and data‑locality benefits of on‑device execution. This makes hybrid AI not just feasible but increasingly essential for building resilient, high‑performance AI systems.
Why is Hybrid Becoming the new Default?
- Optimal balance of performance and cost
High-frequency, low-complexity tasks execute locally for near-instant responses and reduced inference costs, while compute-intensive workloads—such as training and deep reasoning—remain in the cloud.
- Intelligent workload routing
Modern orchestration frameworks dynamically decide where workloads should run based on context, device capability, policy, and accuracy requirements. Lightweight tasks stay on-device, while complex reasoning escalates to the cloud.
- Controlled and compliant data flows
Sensitive or regulated data can remain entirely on-device, while non-sensitive signals move to the cloud for analytics, monitoring, and continuous improvement.
- Unified governance across environments
AI management platforms now support distributed deployments with centralized policy enforcement, monitoring, and auditing across cloud and edge environments.
A Practical Example
Consider a global retailer:
On-device: Handheld scanners and associate devices provide instant product lookup, translation, and customer assistance without relying on connectivity.
Cloud: Advanced demand forecasting, fraud models, and personalization engines run centrally.
Hybrid: Devices classify or summarize information locally, escalating to cloud LLMs for deeper reasoning or cross‑store analysis.
This hybrid pattern is emerging across industries—from manufacturing and healthcare to finance, logistics, and consumer electronics—where enterprises blend the strengths of each environment to build more adaptive, efficient, and resilient AI systems.
Decision Framework: How CXOs Should Evaluate AI Deployment Models
To guide strategic planning, leaders should assess four dimensions.
- Performance Requirements
- Is low-latency critical to safety, user experience, or revenue?
- Can intermittent connectivity be tolerated?
On-device excels when responsiveness is non-negotiable.
- Cost and Financial Model
- What is the expected inference volume?
- How volatile is usage?
A hybrid approach mitigates the unpredictability of per-inference cloud pricing.
- Security, Compliance, and Data Sovereignty
- Does data contain PII, PHI, or regulated attributes?
- Are there cross-border data flows to manage?
On-device helps avoid compliance pitfalls and simplifies governance.
- Model Complexity and Maintenance
- Does the workload require large-context reasoning or massive multi-modal fusion?
- How frequently will models be updated or retrained?
Cloud remains the engine for heavy-lift training and refinement.
From this analysis, most enterprises find that no single environment meets all needs, reinforcing the case for hybrid.
What do Enterprises Need to Build in 2026?
To adopt hybrid AI at scale, organizations should invest in several foundational capabilities.
A. Distributed AI Architecture
Enterprises need an abstraction layer that allows developers to deploy workloads across device and cloud without rewriting logic for each environment.
B. Unified Identity, Security, and Trust Model
Strong attestation, secure enclave execution, and fine-grained data flow policies form the backbone of trustworthy hybrid systems.
C. Model Lifecycle Management
Versioning, A/B testing, rollback, telemetry, and performance monitoring must work seamlessly across both cloud clusters and millions of devices.
D. Edge-Aware DevOps and AI Ops
As devices become intelligent nodes, distributed update pipelines, automated hardware detection, and environment-aware packaging become essential.
E. Governance for Responsible AI
Transparency, fairness, auditability, and safety must be incorporated across both cloud and on-device execution paths.
Predictions for 2026 & Beyond
Looking ahead, several trends will reshape enterprise AI strategy:
- Most enterprise applications will ship with an on-device fallback mode.
- Foundation models will arrive in dual formats: high-capacity (cloud) and optimized (device).
- AI PCs and AI-capable mobile devices will become the default enterprise endpoints.
- Hybrid orchestration engines will evolve into intelligent routers that autonomously decide how to balance speed, cost, and accuracy.
- Regulators will increasingly require data minimization, boosting demand for on-device inference.
The implication is clear: hybrid is not just a technical choice—it is becoming a competitive necessity.
Conclusion: The Future Is Hybrid—By Design, Not by Compromise
Enterprises in 2026 need speed, trust, and cost control to stay competitive. On-device AI brings low latency and strong data control. Cloud AI adds scale, advanced models, and steady improvement. Used alone, each falls short.
A hybrid setup that combines local inference with cloud intelligence offers a practical path forward. It balances performance, resilience, and cost while supporting real business needs.
Teams that build hybrid AI capabilities now reduce risk and deliver better experiences. They also set a clear standard for how AI should work when devices and the cloud are designed to operate together, not in isolation.