A strong enterprise software testing strategy helps teams manage large systems that run constant transactions, data flows, and internal workflows. These systems depend on steady performance across different services.
This requires a testing approach that clarifies how each part behaves during daily operations — something strengthened through our enterprise software testing services that support structured QA across large systems.
Teams need a structure that supports reliable features, clean integrations, and predictable releases. When testing follows a planned direction, updates move across environments without disruption, and issues become easier to detect before they affect operations. This foundation helps organizations maintain stable software and prepare for long-term growth.
Why does enterprise QA matter to large organizations?
Enterprise systems run across multiple teams, regions, and platforms. Each part supports a specific function that needs steady performance throughout the day. This creates a responsibility for organizations to maintain predictability across all software activities. A structured QA process reduces operational risk and supports long-term stability by giving teams clarity on how features behave, how updates move through environments, and how different components depend on each other.
Many enterprise environments also interact with third-party systems that process critical data. These integrations need careful coordination, so information flows smoothly. Some teams also rely on automated workflows that run throughout the product Lifecycle, and these workflows require dependable validation.
Key areas that require attention include:
- Data exchange with external systems
- Automated job execution
- Multi-step transaction processing
- Service-to-service interactions
A short example shows how these factors appear in a real environment: a financial platform may run daily settlement tasks, user activity logs, reporting tools, and cross-service checks. All these tasks require reliable execution, which underscores the importance of enterprise QA.
What challenges do teams face in enterprise app testing?
Enterprise systems operate across distributed architectures, where services run independently and interact through internal channels. This setup brings layers of complexity that require constant oversight. Some services handle large volumes of data; others handle sensitive transactions, and many are frequently updated across environments. With different teams managing different parts, coordination becomes critical.
These conditions reflect the core challenges in enterprise app testing, many of which can be reduced by adopting strong QA automation frameworks that support consistent validation. where a single system change can affect multiple others.
Several areas need focused attention:
- Authentication paths: These flows depend on strict rules, so access remains safe at all times.
- Cross-service movements: Data and requests must pass through multiple layers, and each movement must be clearly validated.
- Internal tools and partner systems: These systems interact with core services and depend on consistent behavior.
- End-to-end activity: Full workflows need validation, so information moves correctly between different parts of the system.
These factors add to the broader challenges in enterprise app testing, and they guide the structure that enterprises follow when designing their testing approach.
What core testing layers form the base of a strong strategy?
A complete testing approach must address the different layers that appear in enterprise systems. Each layer supports a specific area of quality, and together they create a structure that teams can rely on throughout releases.
Core Testing Layers at a Glance
| Layer | Focus | What It Covers | Purpose |
| Functional | Features | Journeys, rules | Correct behavior |
| Integration | Services | Links, data flow | Stable connections |
| Performance | Traffic | Load, stress | Consistent response |
| Security | Access | Permissions, requests | Safe environment |
| Data integrity | Accuracy | Inputs, processing | Reliable information |
These layers reflect how enterprise applications behave during daily operations. Functional testing verifies whether each feature completes its task correctly, as outlined in our guide on functional and integration testing best practices for enterprise apps.
Integration checks confirm that services exchange information reliably. Performance testing reveals how the system reacts under different loads. Security testing ensures that access rules and data handling follow approved standards. Data integrity checks maintain the accuracy of information across the system.
Enterprises rely on these layers because they support predictable behavior throughout the product Lifecycle. When these layers work together, teams maintain confidence during releases and daily system operations. This structure also supports a clear enterprise software testing strategy because the testing layers define the areas that require continuous attention.
How to Build an Enterprise Software Testing Strategy (Step-by-Step)
A strong testing strategy starts by aligning with how your system works and what matters most for your business.
Follow these steps to build a clear, maintainable, and effective enterprise QA strategy that supports long-term stability.
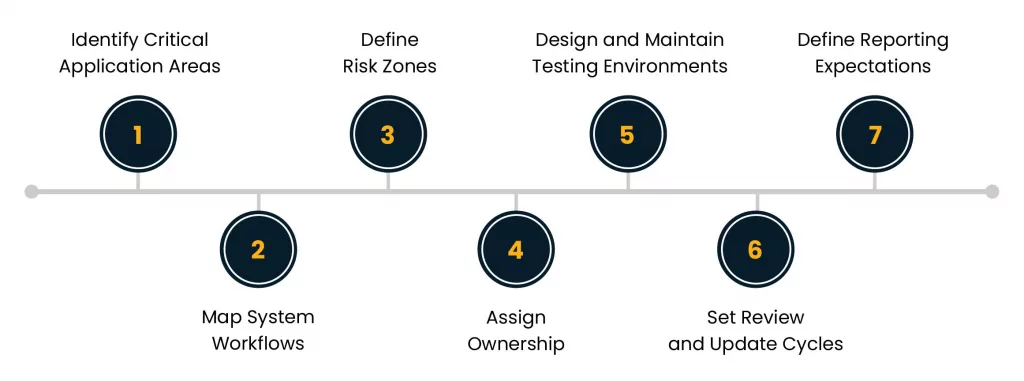
1. Identify Critical Application Areas
- Understand which parts of your system support key business functions.
- Prioritize testing in these areas as they carry out the most operational risk.
2. Map System Workflows
- Outline how data flows across services, endpoints, and integrations.
- This helps spot dependencies and potential risk zones.
3. Define Risk Zones
- Mark out high-risk areas like payment handling, legal compliance, or multi-step transactions.
- Apply stronger testing coverage to these zones to maintain reliability during releases.
4. Assign Ownership
- Allocate responsibilities clearly: who writes, maintains, and runs which tests.
- Include ownership for:
- Functional tests
- Integration points
- Data validation processes
5. Design and Maintain Testing Environments
- Set up environments that mimic production closely.
- Ensure environments are regularly synced and kept consistent throughout the lifecycle.
6. Set Review and Update Cycles
- Conduct test reviews on a set of cadences (e.g., every sprint or monthly).
- Update test scripts as systems evolve to maintain relevance.
7. Define Reporting Expectations
- Decide how test results are shared across teams.
- Include what gets reported (failures, coverage gaps, trends) and how often.
Core Elements of a Good Strategy
Here’s a quick reference checklist of essential pieces your strategy should cover:
| Element | Why It Matters |
| Clear objectives | Focuses effort on what’s most important to the business |
| Workflow mapping | Helps identify weak points and dependencies |
| Test ownership | Avoids confusion and ensures accountability |
| Review schedule | Keeps test suites current and effective |
| Reporting plan | Brings visibility and supports decision-making |
How should enterprises design test automation for long-term stability?
Automation supports continuous testing in enterprise environments — especially when supported by enterprise automation testing solutions designed for scale, and teams begin by selecting test cases that gain the most value from automated execution. Stable functional flows and API checks with predictable patterns fit well here because they work reliably inside CI/CD pipelines and provide steady coverage during each release cycle.
Test data also needs structure, so teams prepare consistent datasets that reflect real scenarios and keep automated runs dependable. As these tests are executed across environments, they help verify updates early and reduce uncertainty around code behavior.
Automation frameworks then require ongoing care, since script failures, broken paths, and data issues need quick attention to maintain stability throughout the release process.
A short checklist helps teams maintain this structure:
- Stable environments for test execution
- Clear scripting guidelines
- Version-controlled test files
- Regular execution schedules
These steps help automation remain dependable and aligned with release cycles. Following these steps also align with essential best practices that support stable QA operations across enterprise teams.
What governance elements strengthen the testing strategy?
A strong governance model keeps QA activity structured, predictable, and aligned with the release process. It also helps teams maintain accountability and visibility as systems evolve. The following elements form the foundation of effective governance:
- Clear ownership for each test area, so teams know exactly which flows they manage and update.
- Updated documentation that explains existing coverage, areas needing new scripts, and features with higher operational impact.
- Defined release checkpoints, ensuring that essential test layers run before any change progresses.
- Risk-based testing paths, which assign deeper coverage to high-impact features and lighter paths to routine updates.
- Audit trails that capture executed tests, the people who ran them, and the results produced.
- Regular review cycles between teams, giving development, QA, and product groups a shared view of current quality levels.
- Quality gates that block unverified changes, helping maintain a consistent release standard.
- Aligned reporting expectations, so leadership gains insight into quality trends and pending risks.
- Structured communication routines, ensuring everyone understands test outcomes and next steps.
These elements work together to keep governance stable and aligned with established best practices for enterprise QA.
Closing Notes!
Enterprise systems require steady attention throughout development, testing, and release cycles. A structured approach helps teams validate features, coordinate integrations, manage automation, and maintain compliance. A mature enterprise software testing strategy supports predictable operations and gives organizations the confidence to release updates consistently. When teams follow clear processes and maintain well-defined responsibilities, the strategy becomes a dependable foundation for long-term enterprise quality.