Introduction – Growing scrutiny in GST compliance & fraud cases
Technology served as the foundation for the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system, which produced an unparalleled digital trail for each transaction. Tax authorities now have strong new tools to keep an eye on taxpayers thanks to digitization, which has increased scrutiny of GST compliance and greatly boosted the number of fraud cases detected.
The statistics highlight the growing risk: during the previous five fiscal years (FY 2020–21 to FY 2024–25), Central GST field officers found 91,370 cases of tax evasion totalling about ₹7.08 lakh crore. Over ₹2.23 lakh crore in GST evasion was detected in FY 2024–2025 alone, with ₹58,772 crore of that amount specifically attributable to Input Tax Credit (ITC) fraud (Source: The Economic Times).
For banks, insurers, and NBFCs, unreliable GST filings directly affect underwriting accuracy, borrower assessment, fraud checks, and portfolio risk — making GST Business Intelligence (GST BI) a critical governance pillar. Businesses can no longer depend on manual procedures in these high stakes landscape. They require a proactive defence. The strategic application of data analytics to go beyond simple return filing and toward ongoing, self-auditing, and strong tax risk management is this shield, which is GST business intelligence in compliance.
To support this shift toward automated GST risk monitoring, businesses can leverage advanced GST business intelligence reports that offer real-time insights and comprehensive compliance visibility.
How Business Intelligence Supports GST Compliance
Effective GST compliance monitoring is now a continuous process, rather than a month-end rush. GST BI tools automate the reconciliation and verification processes that are critical for avoiding penalties and ensuring cash flow integrity.
1. Return Filing Accuracy:
BI systems automatically cross-validate data across internal ERPs, accounting software, and the GSTN portal – GSTR-1, GSTR-3B. This ensures that the figures reported are consistent and accurate, minimizing manual data entry errors.
2. Reconciliation Automation:
GST Return Reconciliation forms the backbone of compliance wherein matching the business’s purchase register is done with the reflected data of the supplier in GSTR-2B. Automated reconciliation tools can handle millions of invoices, flagging mismatches instantly. For BFSI, this automation becomes quite important because manual reconciliation is highly prone to errors, especially at high-volume transactions.
3. Anomaly Detection:
By analysing historical trends, BI platforms identify deviations in the tax payable, ITC claimed, or turnover reported. For instance, a sudden, disproportionate jump in ITC claims relative to turnover can trigger a warning, allowing the finance team to investigate before the anomaly is flagged by the tax authorities’ own advanced analytics models.
GST BI in Fraud Prevention
The government has successfully leveraged Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to detect fraud by identifying abnormal transaction patterns, with over 15,000 ITC fraud cases detected in FY 2024-25 alone (Source: The Economic Times). Businesses must adopt similar GST fraud analytics to protect themselves.
- Identifying Fake Invoicing and Circular Trading: Sophisticated GST business intelligence systems use ML algorithms to map relationships between suppliers, buyers, and intermediaries. They can detect patterns indicative of shell entities, circular trading (where goods or services exist only on paper), or unusually rapid growth in transactions with new, unknown vendors, which are common indicators of GST evasion detection.
- Vendor Risk Management: A key challenge is relying on suppliers with poor compliance histories. GST BI platforms assign risk scores to vendors based on their GSTR-3B filing regularity. Non-compliant vendors can lead to the denial or reversal of the recipient’s ITC. BI enables the business to follow up proactively with such high-risk vendors or even disengage to preserve the cash flow.
- Suspicious Transaction Monitoring: Software solutions can monitor real-time invoice-level data for conditions like:
- Mismatch in HSN codes between inward and outward supplies.
- Inconsistent inter-company transaction values.
- Frequent blocking of a vendor’s E-Way Bill (EWB) or ITC status.
Tools & Techniques in GST BI
The transformation of GST data insights into actionable steps relies on modern analytical techniques:
1. Customisable Dashboards
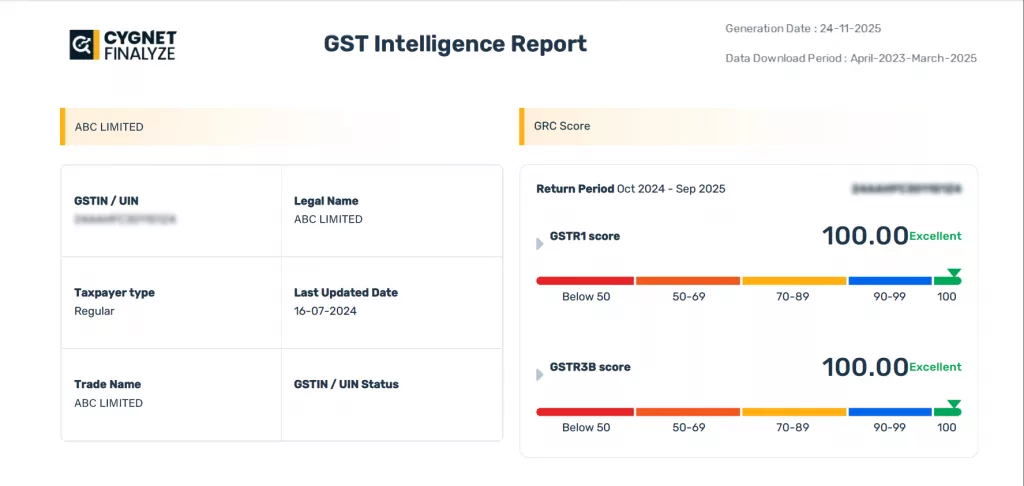
These provide a visual, real-time summary of the company’s GST compliance monitoring status. KPIs include GSTR-2B vs. Purchase Register mismatch percentage, tax liability trends, and vendor compliance scores.
2. Predictive Analytics
ML algorithms use historical filing behaviour, industry benchmarks, and transaction data to forecast the probability of receiving a GST notice or facing an audit. This allows the tax team to prioritize remedial actions.
3. AI-Driven Checks
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is increasingly used to analyze unstructured data, while ML-based risk scoring models help both the government and companies focus on high-risk cases.
Challenges Businesses Face
Despite the benefits derived, systemic challenges have made it difficult for many businesses to fully implement the GST business intelligence:
1. Data Silos and Integration Issues
Financial data is split across various ERP systems, accounting software, and subsidiary branches, making the processing of data from a single location difficult. Seamless API integration with GSTN and internal systems remains a challenge.
2. Reliance on Manual Reporting
Most of the SMEs still use manual reconciliation with spreadsheets. These are highly prone to errors and cannot support the complexity and volumes of daily transactions.
3. Lack of real-time alerts:
Without any automated system, businesses usually discover compliance breaches or vendor non-filing once the GSTR-2B is generated, which may become too late for them to act upon. Consequently, this leads to blocked ITC and results in cash flow issues.
4. Constant Regulatory Change
The dynamic nature of GST laws necessitates continuous updates of software and training of staff, thus burdening the internal resources.
Best Practices for GST BI Adoption
Implementing GST business intelligence in compliance requires a strategic shift and not just a software purchase.
1. Centralized Data Management
Integrate all transactional data regarding e-invoices, EWBs, and internal records into one source that the BI platform can access. This will provide a single source of truth for all GST reporting.
2. Automation of Core Compliance
Invest in tools that automate GSTR-2B reconciliation, GSTR-1/3B cross-validation, and generation of filing reports. This reduces human error and frees up the tax professional to perform more strategic tasks of tax risk management.
3. Proactive Vendor Compliance System
Automate a system of communication with non-compliant vendors by sending mismatch reports and a clear follow-up trail to mitigate the loss under ITC.
4. Regular Internal Audits
Conduct periodic mock GST audits using the BI insights to identify and rectify compliance gaps before external authorities do.
Conclusion – Using GST BI as a shield for compliance and fraud control
GST business intelligence in compliance is rapidly transitioning from a desirable feature to an operational necessity. By leveraging GST fraud analytics and automated reconciliation, a robust BI solution acts as a preventative shield, minimizing penalties, maximizing eligible ITC, and safeguarding the business from involvement in fraudulent supply chains. Cygnet’s GST Business Intelligence (BI) solution empowers businesses to stay ahead of compliance challenges by automating real-time reconciliation, flagging discrepancies, and providing actionable insights for tax optimization.
 FAQ’s
FAQ’s
1. What is GST Business Intelligence (GST BI)?
GST BI refers to analytics tools that process GSTN data to improve compliance, detect fraud, and monitor vendor risk.
2. How does GST BI help BFSI institutions?
Banks, NBFCs, and insurers use GST BI for borrower verification, turnover validation, fraud detection, and portfolio monitoring.
3. Can GST BI detect fake invoicing or circular trading?
Yes. ML models map supplier-buyer networks to identify abnormal transaction flows.
4. What business problems does GST BI solve?
It eliminates manual reconciliation, flags ITC mismatches, monitors vendor filing patterns, and reduces compliance penalties.
5. Is GST BI necessary if my business files returns regularly?
Yes. Regular filing does not protect against vendor non-compliance, mismatches, or unnoticed anomalies.