Many businesses are transitioning away from legacy database platforms, such as Microsoft SQL Server. Why? Because:
- Maintenance is high
- Licensing is expensive
- Scalability is limited
Cloud-native databases like Amazon Aurora and PostgreSQL provide modern features as well as automatic scaling. Moreover, they also make it easier to integrate with cloud infrastructure.
Nevertheless, if your team is considering a SQL Server to Aurora migration, then planning is key. The goal isn’t limited to shifting data. It also goes to:
- Maintaining application logic
- Avoiding disruptions
- Taking advantage of long-term performance improvements
This blog guides you through the full modernization process. As a result, you can make informed decisions without compromising critical systems.
Technical Differences Between SQL Server vs Aurora PostgreSQL
Migrating from SQL Server to Aurora PostgreSQL involves more things than moving tables and queries. These platforms work differently under the hood. Hence, comprehending the technical contrasts early helps avoid compatibility issues during migration.
Here’s a table comparing the two:
| Feature | SQL Server | Aurora PostgreSQL |
| Language | T-SQL | PL/pgSQL, standard PostgreSQL |
| Transaction Model | Snapshot Isolation, Read Committed | MVCC-based concurrency control |
| Indexing Options | Clustered, non-clustered, XML, spatial | B-tree, BRIN, GIN, GiST, expression indexes |
| Storage | Monolithic engine | Distributed, cloud-native storage |
| High Availability (HA) | Always On, Failover Clustering | Multi-AZ support, auto-healing replicas |
| Extensions and Tooling | Limited custom extensions | JSONB, PostGIS, full-text search, TimescaleDB |
Migrating to Aurora means adopting PostgreSQL standards. Some SQL Server features may not have direct equivalents in Aurora PostgreSQL, like
- SQL CLR
- Indexed views
- Certain XML data types
Identifying these early is a critical step in any SQL Server to Aurora migration.
Pre-Migration Planning
Effective planning avoids surprises. So, it is essential to evaluate your current workloads and understand what adjustments are required.
Here’s what this planning phase looks like in practice:
1. Inventory All Existing Workloads
- List every application that connects to your SQL Server instance.
- Identify the following:
- all stored procedures
- triggers
- linked servers
- custom logic
- Use AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) and AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) to run an assessment report.
2. Feature Compatibility Check
- Use SCT to highlight which SQL Server features aren’t supported in Aurora PostgreSQL.
- Incompatibilities often include proprietary functions or T-SQL constructs.
3. Tooling Choices
- Babelfish for Aurora PostgreSQL allows SQL Server applications to talk to Aurora using the TDS protocol. This is helpful when you want to reduce code rewrites during migration.
- AWS DMS handles full data load and change data capture (CDC).
- SCT converts schema objects and flags incompatibilities.
4. Performance Benchmarking
- Capture current SQL Server performance baselines: CPU, memory usage, IOPS, latency, and query plans.
- You’ll need this for post-migration comparison and tuning.
5. Sizing for Aurora
Aurora decouples storage and compute. Start with an instance class that closely matches your SQL Server environment, then adjust after testing.
Step-by-Step Process: SQL Server to Aurora migration
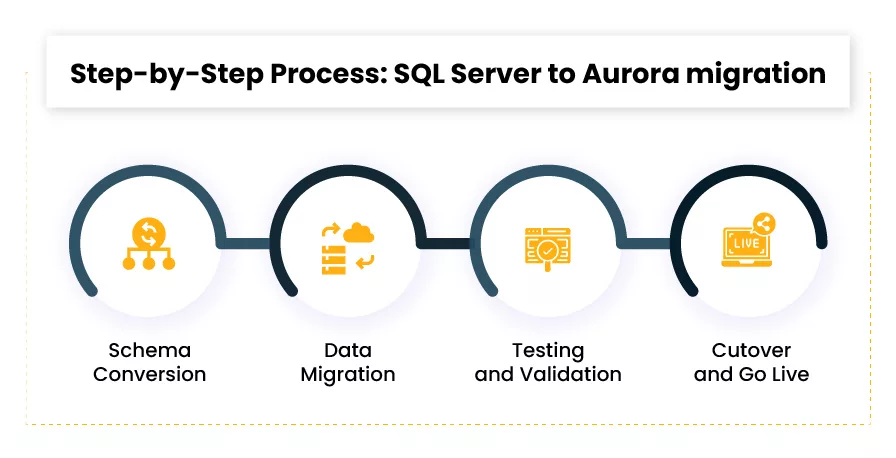
A well-structured process ensures success. Here’s how teams can migrate their workloads methodically:
Step 1: Schema Conversion
- Run AWS SCT to scan and convert your schema from SQL Server to Aurora PostgreSQL.
- Review and manually adjust any schema objects that SCT flags.
- Validate all data types — for example,
datetime2in SQL Server maps totimestampin PostgreSQL, but formatting and precision must match.
- Create a target schema in Aurora after cleaning up conversions.
Step 2: Data Migration
- Use AWS DMS to migrate data. Start with a full load of all tables, followed by continuous replication via CDC.
- Tune migration settings to handle batch sizes, LOB handling, and memory usage.
- Make sure foreign keys and constraints are disabled during bulk load to avoid errors.
Step 3: Testing and Validation
- Run application integration tests using staging Aurora endpoints.
- Compare results from both systems using checksums or record-level validation.
- Run performance load tests and tune:
- Autovacuum
- Work_mem
- Shared_buffers
Step 4: Cutover and Go Live
- Once testing is complete and delta replication is caught up, schedule a cutover window.
- Update your app configurations and DNS routing to point to Aurora.
- Monitor performance closely during the initial go-live phase.
This process ensures your SQL Server to Aurora migration is not rushed — it’s measured and built around risk mitigation.
Even when the steps are clearly mapped, testing remains critical to avoid service interruptions. Ensuring workload continuity during and after the switch requires validation of both functional behavior and query performance.
PostgreSQL Modernization After Migration
Now that your system is running on Aurora PostgreSQL, you can start modernizing beyond just migration.
Refactor T-SQL Logic
- Convert SQL Server stored procedures to PL/pgSQL where possible.
- Revisit control-of-flow logic and system function calls.
- PostgreSQL handles exception management and variable declarations differently from T-SQL.
Adopt PostgreSQL-Native Features
- Use JSONB for storing flexible schema data, which outperforms SQL Server’s XML columns.
- Implement table partitioning to manage large datasets with performance benefits.
- Add GIN or GiST indexes for search-heavy applications.
Extend Capabilities with Extensions
- Install PostGIS if your application needs spatial queries.
- Use pg_stat_statements to track slow queries.
- Leverage pg_partman for automated time-based partitioning.
Build CI/CD Workflows for Database Changes
- Use programs like Flyway or Liquibase to incorporate schema updates into your workflow.
- Organize your database modifications according to development sprints by using version control.
With these modifications, the PostgreSQL modernization cycle is finished, and the database gradually improves in terms of:
- Maintainability
- Scalability
- Performance
Practical Walkthrough: Migrating a Customer Orders Database from SQL Server to Aurora PostgreSQL
Say you run a retail analytics platform. It uses Microsoft SQL Server to store customer order data. Now, you are planning to move that to Aurora PostgreSQL. The major aim here are two things:
- To cut down on licensing costs
- Get ready for better scalability
Here’s how the team could complete the full migration:
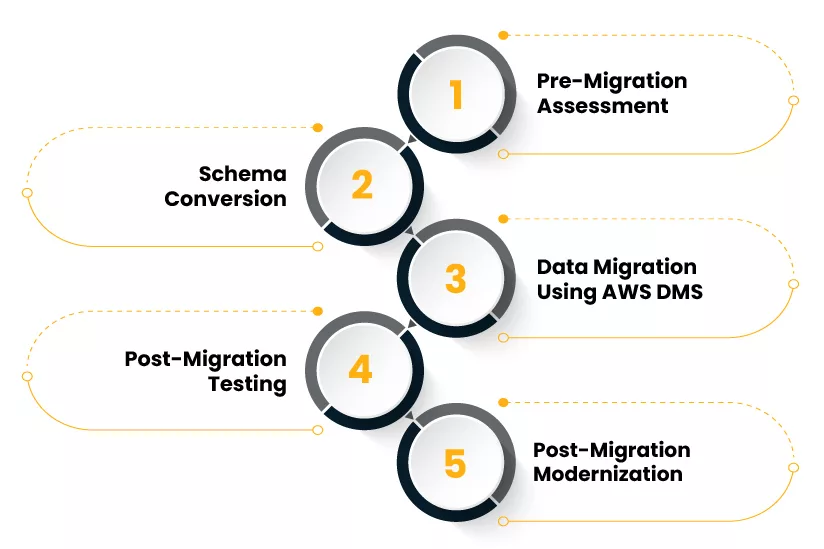
Step 1: Pre-Migration Assessment
- Run AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) on your SQL Server instance.
- The SCT report shows that 95% of the schema is compatible, but highlights:
- One stored procedure uses
MERGE, which isn’t directly supported. - A column uses
sql_variant, which maps totextin PostgreSQL.
- One stored procedure uses
- You decide not to use Babelfish due to the custom functions involved.
Step 2: Schema Conversion
- Use SCT to convert the schema.
- Review the generated DDL and manually fix:
- Replace
MERGElogic withINSERT ... ON CONFLICTin PostgreSQL. - Adjust identity columns using PostgreSQL sequences (
SERIALorGENERATED BY DEFAULT).
- Replace
Example adjustment:
SQL Server:
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderId INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerId INT,
TotalAmount DECIMAL(10,2)
);PostgreSQL:
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderId SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerId INT,
TotalAmount NUMERIC(10,2)
);Step 3: Data Migration Using AWS DMS
- Create an AWS DMS task to do a full load + CDC (change data capture).
- Monitor replication lag. Keep replication running for 3 days to validate CDC.
- During replication, the test application reads from the Aurora read replica.
Step 4: Post-Migration Testing
- Run test queries to compare the row counts, sums, and aggregate results.
- Validate indexes are working as expected using
EXPLAIN ANALYZE.
- Enable
pg_stat_statementsfor performance visibility.
Sample validation query:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Orders WHERE OrderDate >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '30 days';Step 5: Post-Migration Modernization
- Convert a frequently used stored procedure from T-SQL to PL/pgSQL.
T-SQL (SQL Server):
CREATE PROCEDURE GetTopCustomers
@MinOrderCount INT
AS
BEGIN
SELECT CustomerId, COUNT(*) AS OrderCount
FROM Orders
GROUP BY CustomerId
HAVING COUNT(*) > @MinOrderCount;
END;PostgreSQL:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION GetTopCustomers(min_order_count INT)
RETURNS TABLE(customer_id INT, order_count BIGINT) AS $$
BEGIN
RETURN QUERY
SELECT CustomerId, COUNT(*) AS OrderCount
FROM Orders
GROUP BY CustomerId
HAVING COUNT(*) > min_order_count;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;- Add auto-scaling read replicas for analytics workloads.
- Schedule weekly
ANALYZEto keep PostgreSQL statistics fresh.
Outcome
- Cut over to Aurora PostgreSQL with just 20 minutes of downtime.
- Reduced database licensing costs by $4,800 per year.
- Performance improved on large analytical queries due to optimized indexes and Aurora’s read scaling.
Final Thoughts!
Businesses modernizing their database stack should consider SQL Server to Aurora migration not just for cost, but for long-term maintainability and performance.
Aurora PostgreSQL brings many benefits:
- Reduced overall cost of ownership
- High availability and cloud-native scaling
- An expanding tool and extension ecosystem
The crux here is to do it correctly. You need to plan every stage, from schema conversion to PostgreSQL modernization. The result? A more seamless transition and improved results.
Do not hurry the procedure if your company needs assistance with database migration AWS. Find the right help and migrate confidently.