Businesses today are expected to deliver digital services at a much faster pace. These include things like customer portals and payment systems. They also need to maintain reliability while being able to handle growth.
But older systems often get in the way. They cannot keep up with the speed or scale that modern services demand. That is why many teams are shifting their focus to cloud modernization and cloud native application development.
This approach gives businesses a way to build applications that work well in cloud environments from the start. However, it is not about taking old software and moving it to the cloud. Cloud native refers to building applications specifically for cloud environments. These applications are designed to be efficient and easy to update as business needs evolve.
To understand why this shift is happening, let’s look at what’s driving businesses toward this approach.
Why Are More Businesses Going Cloud Native?
People expect digital services to run without issues. They also notice when updates take too long. As a result, businesses now face pressure to keep things moving while staying in control of their costs and decisions.
Many organizations, including small businesses, are now using cloud native development services to make this possible.
Some examples include:
- A retailer preparing for holiday traffic without downtime
- A financial service company releasing weekly updates
- A health provider offering seamless online booking
They all need systems that are built to adapt. That’s where cloud native application development helps.
What Does ‘Cloud Native’ Actually Mean?
Cloud native is a way of building apps that are meant to run in the cloud from day one. They’re set up to use everything the cloud offers, including:
- How they’re launched
- How they grow
- How they’re looked after
This approach often relies on container technology and automated processes. It also supports modular structures that can grow or adjust as needed. These systems are built to manage changes and recover from failures with more control — a core capability of cloud engineering services.
An app built in this way can:
- Start up faster
- Use only the resources it needs
- Handle sudden traffic spikes
- Roll out new updates with low risk
These traits are hard to achieve with older, traditional methods.
How Is It Different from Traditional Software?
Older software is usually built as a big system. If something needs to change, it can affect the whole thing. Even a small update might mean shutting everything down or checking every part just to be safe. That process takes time and can cause problems.
Cloud-native software breaks this down into separate units that can run independently.
Here’s a quick table to show the difference:
| Feature | Traditional Software | Cloud Native Software |
| Structure | One large system | Small, independent parts |
| Deployment | Manual, slow | Automated, faster |
| Scalability | Requires major effort | Built-in scalability |
| Updates | Risk of downtime | Minimal disruption |
| Cost Efficiency | Overprovisioned | Use-what-you-need |
This kind of modular design is made possible through cloud-native microservices and orchestration tools.
What Are the Key Parts That Make Cloud Native Work?
A cloud-native approach includes several technical pieces. These aren’t just buzzwords — they’re the backbone of how modern applications run well in the cloud.
Key Components:
- Microservices
Each service or feature is separated into its own unit. For example, user login, payments, or search might each be their own service. This allows teams to update or scale one piece without affecting the rest.
- Containers (e.g. Docker)
These packages up software, so it runs consistently in any environment. Whether it’s development, testing, or production — the container behaves the same.
- Kubernetes
A system used to manage and run many containers at once. It automates deployment, scaling, and operations.
- DevOps & Automation
Instead of manually releasing updates or fixing problems, many tasks are automated. This means faster changes and fewer human errors.
Together, these tools support cloud native architecture, enabling agility and faster delivery.
Why Should Business Owners Care About This?
This approach affects how a business delivers value to its customers. Here’s how:
Faster Time to Market
You can launch new features more quickly. If customers request something or you spot a new opportunity, your team can move fast.
Less Downtime
Apps built this way tend to run more smoothly. If one part stops working, the rest can still keep going. There is no need to shut everything down.
Better Use of Developer Time
Teams can focus on solving business problems, not fixing servers, or waiting on long deployments.
Scalability Without the Overhead
Your app can handle 10 users or 10,000 users. Plus, you do not need massive changes.
Using cloud native development services lets even smaller teams compete with much larger ones.
Is This Just for Big Tech Companies?
No, it is not just for companies like Amazon or Netflix. While they may have introduced the approach early on, cloud native application development is now practical for businesses of all sizes.
You do not need to build everything yourself. Platforms like Google Cloud and AWS already have tools set up. Even small teams can start using them without needing a big technical setup.
Many businesses are already working this way. A retail brand might use it to manage changing website traffic. A health provider might rely on it to keep online services running. Even finance and education teams are using it to release updates more consistently and reduce system issues.
The approach works because it fits real business needs — not just big tech goals.
What Can Cloud Native Look Like in Your Business?
The following are common scenarios that benefit from a cloud-native approach.
Examples:
- A retail website often gets a rush of visitors during end-of-year sales. With cloud-native tools, the site can handle that traffic. The site does not slow down.
- A healthcare provider offering 24/7 telehealth booking. If one service fails, the system can keep other parts running smoothly.
- A finance platform that updates security protocols weekly. Cloud-native tools allow these updates without full system shutdowns.
These are real ways to use cloud native microservices and containers to meet customer demand and maintain trust.
How Can You Start with Cloud Native?
You do not need to move everything at once. In fact, starting small is often better.
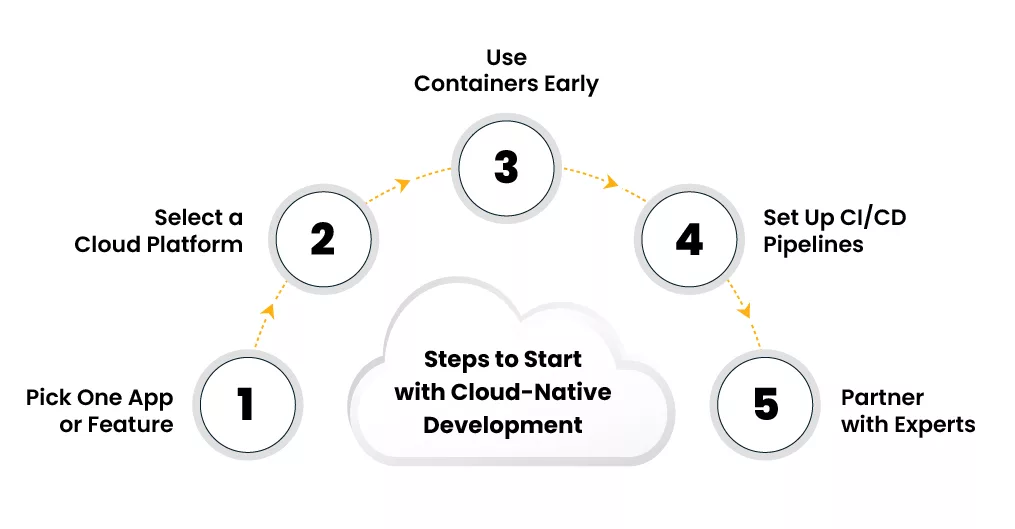
Here’s a simple path forward:
1. Pick One Application or Feature
Choose something like your online checkout, customer dashboard, or booking system.
2. Select a Cloud Platform
Use services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. They all offer tools that support cloud native development services.
3. Use Containers from the Start
Even small apps run more smoothly when placed in containers. It makes future changes easier.
4. Set Up CI/CD Pipelines
Tools like CI/CD help teams make changes without slowing things down or causing issues.
5. Work With Experienced Developers or Partners
If your team has not worked with cloud native architecture before, you should get a cloud migration consultant to help you get started safely.
This step-by-step method helps reduce risk while giving you early wins.
What’s Coming Next in the Cloud Native World?
Serverless Platforms
Let you run code without managing any servers at all.
Edge Computing
Moves parts of your app closer to the user’s physical location for faster performance.
AI Integration
Today’s platforms come with built-in tools, so you do not need a full data team to build smart features into your app.
Is Now the Right Time to Go Cloud Native?
Yes. If your business is growing, or even if it just needs to keep up with customers better, this approach is worth exploring.
Cloud native application development gives you the tools to stay reliable and reduce technical bottlenecks.
The process might seem technical at first, but the benefits are very real — especially when you use cloud native development services designed for your size and industry. Get started today!