Introduction
e-Invoicing UAE is part of the larger digital initiative to fully digitize the country’s tax administration system and to streamline the electronic billing UAE framework. The goal is to reduce errors and paper usage, prevent fraud and tax evasion, and ensure seamless VAT and e-Invoice regulation UAE compliance for all registered entities.
UAE e-Invoicing implementation is not yet mandated for businesses, but starting from approximately July 2026, phase 1 of the UAE e-billing system rollout—based on the size or turnover of the business—will begin after providing sufficient lead time for successful implementation.
UAE e-invoicing Regulations & Compliance
For more detailed information, kindly visit our blog on the UAE e-invoicing mandate.
Benefits of E-Invoicing in UAE
Invoicing offers broad benefits, which is why countries worldwide, including GCC members like KSA and the UAE, have already started embracing it. UAE’s transition toward digitization—through electronic billing UAE—represents a strategic step to automate and modernize its tax ecosystem.
UAE e-Invoicing implementation provides numerous benefits: optimized tax processes, faster e-Invoice processing, automation in workflow, reduced manual errors, fraud prevention, enhanced efficiency, improved tax calculation accuracy, and better handling of cross-border transactions. These collectively ensure better tax compliance and reporting.
Recognizing these advantages, the FTA is working to make the UAE e-billing system operational soon.
Challenges in UAE E-Invoicing Adoption and How to Overcome Them
While the e-Invoicing process delivers immense value, several challenges must be managed effectively. Common issues include ERP integration with UAE portals and access points, legacy system incompatibilities, data validation concerns, limited awareness of new UAE e-Invoicing regulations, and maintaining data security and privacy.
These challenges are issue related to integration of ERP with UAE portals and access point due to legacy or non-compatible systems, stakeholders’ resistance to change, unavailability of invoice data, data validation, handling advanced technologies, scattered data, data storage limitations, lack of knowledge of new regulations and legislation, security and privacy concerns, invoice tampering, working with multiple service providers for different services etc. The list of challenges can go on if not handled properly.
To overcome these, businesses should select an experienced Accredited Service Provider UAE, follow the right UAE implementation guide, and train their teams to adopt the new system efficiently.
While this is a glimpse of the benefits and challenges faced in UAE e-invoicing implementation, read the UAE e-invoicing complete guide for a detailed view.
Step-by-Step E-Invoicing Implementation Guide
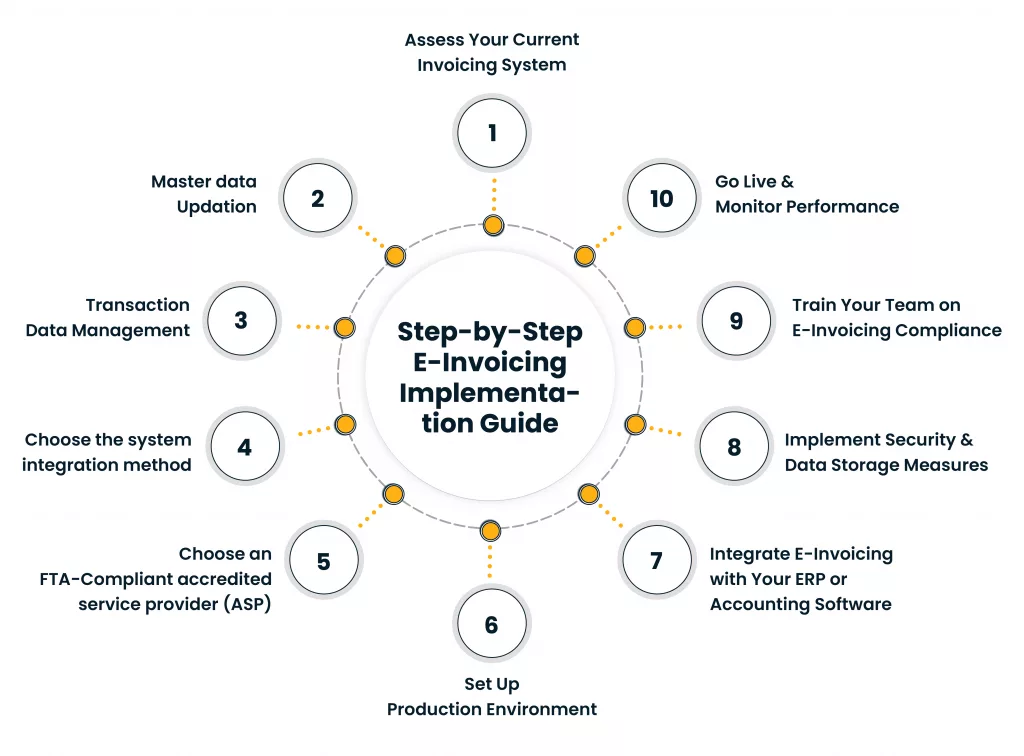
Start your e-invoicing solution implementation journey early to ensure there is sufficient time to design the e-invoicing process architecture, select the ideal service provider, evaluate compliance requirements, identify gaps, align the process across the departments, and smoothly implement and monitor it. The UAE e-invoicing solution implementation step-by-step process is as follows:
Step 1: Assess Your Current Invoicing System
The first and foremost step for an e-invoicing system implementation is examining the existing infrastructure and systems.
Identify the existing process for invoices received or issued and understand how the invoice data is validated and corrected in case of discrepancies.
Identify the source of invoice data, i.e., ERP, legacy systems, POS, invoicing tools, etc, if invoices are generated from various modules or front-end billing systems. Evaluate potential gaps in existing invoicing systems and processes and their compatibility with FTA requirements.
Step 2: Master data Updation
There are 50 mandatory fields required for the generation of standard tax invoices and 49 mandatory fields for the generation of commercial tax invoices. While for VAT compliance, 15 fields out of the 50 and 16 out of the 49, respectively, were not required.
Therefore, taxpayers may not have information related to those fields in their master data, which is mandatorily required for FTA-compliant e-invoicing requirements.
Review current master data for the supplier and customers, verify their names, TRN, locations, VAT registration numbers, and other related details.
Remove unwanted details and add additional details as required for the mandatory fields of e-invoicing regulation.
It is essential to have digital customer and supplier onboarding to ensure an automated record of master data, along with verification.
Step 3: Transaction Data Management
Evaluate business services and products and identify and categorize the type of transactions (B2B, B2C, B2G, RCM), document type (standard tax invoice, commercial Invoice, CN, DN, purchase order), applicable tax codes, rates, etc and ensure that correct e-invoice document is generated based on the transaction type and the tax is calculated based on applicable tax rate.
Test each e-invoice generation with different transaction types under different scenarios, such as normal transaction, discounted transaction, multiple currency transactions, continuous supply, exports, etc., to ensure each e-invoice is generated in PINT-AE format as per FTA’s e-invoicing compliance requirements.
Also perform compliance check, integration testing, current performance evaluation, security measure, etc to ensure the system is compatible with the compliance requirements.
Step 4: Choose the system integration method
Integration of ERP, UAE portal, e-invoicing solution, PEPPOL access points, etc, is vital to ensure end-to-end automated flow of e-invoice. There are various methods available for the integration of the entire system, such as API connectivity, SFTP, DB SSIS, and more.
Choose API for real-time transfer and updates, select SFTP for scheduled and secured transfer, DB for centralized data sharing, or SSIS for complex workflow integrating multiple data sources.
Business may evaluate their business infrastructure and the security policies and accordingly select the ideal integration method as per their business requirement, ensuring an FTA-compliant e-invoicing process.
Look for plug-and-play connectors or customized middleware that ensures your ERP modules (such as finance, procurement, or sales) can effortlessly communicate with the e-invoicing platform.
Step 5: Choose an FTA-Compliant accredited service provider (ASP)
It is vital for business organizations to select a UAE authority-approved, ASP and evaluate their expertise and experience in field of e-invoicing and other indirect tax compliance services across the globe.
Further, evaluate the key features they provide to ensure the UAE digital e-invoicing system is aligned with the business as well as the UAE authorities’ required criteria.
It is essential to have a single source of truth, meaning a platform that provides all requirements of indirect tax automation and compliance. Some of the other important features to look for are end-to-end process automation, real-time validation, integration with UAE’s official portal for reporting, seamless integration with PEPPOL’s access points, built-in compliance check, AP and SMP capabilities, error-free transmission of e-invoices and other documents, preference to choose cloud-based or on-premises data environment , etc.
Step 6: Set Up Production Environment
Choose between on-premises, private cloud, or public cloud implementation after evaluating their pros and cons with specific business needs such as scalability, control, cost, etc, and set up the infrastructure for its actual production.
Ensure that system architecture, such as servers, networks, integration, etc., is fully compatible with e-invoicing architecture and is deployment-ready.
Step 7: Integrate E-Invoicing with Your ERP or Accounting Software
The E-invoicing system and the business’s ERP and accounting software integration are vital to ensure the generation of e-invoices in the familiar system, the easy transmission of e-invoices among ERP, UAE authorities, and accredited access points to get real-time reporting and updates on e-invoice status with minimal changes in the current ERP and e-invoicing workflow.
An ideal e-invoicing solution must be easily integrated via any integration method such as API, SFTP, DB SSIS , ensuring scalability and flexibility for current and future business needs and ensuring that all required compliance and validation checks are followed.
Step 8: Implement Security and Data Storage Measures
The most vital requirement for any software is its security features, as it is important to ensure that all sensitive data is secured and encrypted to avoid the risk of data leakage, intrusion, data tampering, forgery, errors, etc.
The invoice data in transit or at rest must be properly encrypted and secure, and only authorized persons can have access to such data to avoid financial and reputational loss.
The e-invoices must be time-stamped and validated to ensure their authenticity and security.
Other security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, password protections, data encryption, audit trails to track invoice activities, role-based access management, firewall protection, etc, should be implemented.
Further, the ASP must comply with security measures and certifications as required by the UAE authorities.
Step 9: Train Your Team on E-Invoicing Compliance
Resistance to change is a common obstacle that companies face while undergoing various infrastructure and workflow upgrades and changes.
While implementing e-invoicing compliance in UAE businesses is mandatory in the coming years, it is vital for businesses to start educating their finance, sales, and IT teams about UAE e-invoicing implementation.
Conduct webinars, educational sessions, and QA sessions to create self-learning tutorials, modules, etc., to make them aware of upcoming mandates, amendments, implementation timelines, and regulatory updates to stay compliant with the law.
Further, ensure that the respective team is familiar with the new workflow and e-invoicing system. Conduct demos and test transactions before going live to ensure the e-invoicing implementation is as per regulatory requirements.
Step 10: Go Live & Monitor Performance
After selecting the ideal e-invoicing system and integrating it with a business ERP solution, it is time to go for live implementation of e-invoice generation and workflow to ensure the solution is aligned with business as well as FTA compliance needs.
Further, there should be regular performance monitoring to ensure there are no errors or anomalies in the process, and the systems must be updated regularly to ensure they are aligned with growing business needs and changing government regulations.
Key Implementation Timelines in UAE e-invoicing
UAE e-invoicing implementation phases
Main Implementation timeline
| Timeline | Implementation |
| Q4 2024 | Development Service Providers’ certification requirements and procedures & Development of UAE Data Dictionary |
| March 2025 | Launching of a dedicated portal for accreditation of service providers for UAE e-invoicing |
| April 2025 | Introduction of PINT AE & Testbeds |
| Q2 2025 | Issuance of e-invoicing legislation |
| July 2026 | Phase1 to go live for reporting |
| On the Horizon | Potential inclusion of B2C transactions |
The implementation of e-invoicing compliance will be in a phased manner, where businesses will start complying with e-invoicing at their required phase, giving sufficient time and prior notice for them to integrate e-invoicing in their business workflow in advance of their requirements coming into mandate.
Why trust Cygnet for UAE e-invoicing implementation?
Cygnet, an approved, accredited service provider, offers PEPPOL-enabled e-invoicing solutions that assist UAE businesses in complying with the Federal Tax Authority’s upcoming e-invoicing mandate, set to commence in July 2026.
With Cygnet, we ensure end-to-end support and services start from evaluation of your existing system, infrastructure, process, and security measures, etc, and facilitate e-invoicing workflow architecture development, deployment, testing, and more based on your business requirements and FTA’s compliance requirements.
The solution offers quick ERP/POS integration, real-time invoice validation and reporting, and flexible deployment options, including on-premises or cloud-based solutions tailored to UAE requirements.
It ensures enhanced data security with end-to-end encryption and is scalable for bulk e-invoice generation. By streamlining the e-invoicing process, Cygnet enables businesses to achieve compliance efficiently while enhancing operational efficiency.
Conclusion & Next Steps
To stay ahead of regulatory change, businesses in the UAE must begin preparing for e-invoicing adoption now. While full enforcement is still a year away, early planning ensures seamless integration, reduces compliance risks, and enables smoother transitions.
Choosing a future-ready, FTA-compliant solution like Cygnet’s e-invoicing solution and investing in internal training can help businesses unlock the benefits of automation, accuracy, and fraud prevention. Partner with experienced solution providers who understand the UAE’s evolving e-invoicing framework and can offer end-to-end support from assessment to go live.