Security problems in the cloud rarely begin with a major incident; they usually start with something small, such as a missed update, an open storage bucket, or an old account still holding access. Over time, these gaps turn into serious risks.
Now, as more businesses move critical systems and data to the cloud, the pressure to keep that environment secure grows fast. From customer platforms to internal tools, cloud infrastructure now supports much more than file storage.
Nevertheless, flexibility comes with complexity, and that’s where security challenges begin.
Securing cloud infrastructure requires an active, ongoing approach—built into everyday operations.
In this blog, we’ll look at the practical steps every business should be taking now to protect their cloud environments.
Understand What You’re Securing
Before you do anything else, you need to know what your cloud setup includes. Many businesses operate across multiple cloud providers, which means systems, users, and data are spread out.
Start with:
- A full list of services, applications, and platforms in use
- All user roles and permissions connected to each system
- Data locations—where it’s stored, processed, and transferred
- Network connections between cloud and on-premise environments
Getting this information together is a basic step in securing cloud infrastructure. You can’t protect what you don’t see or understand.
How to Secure Cloud Infrastructure?
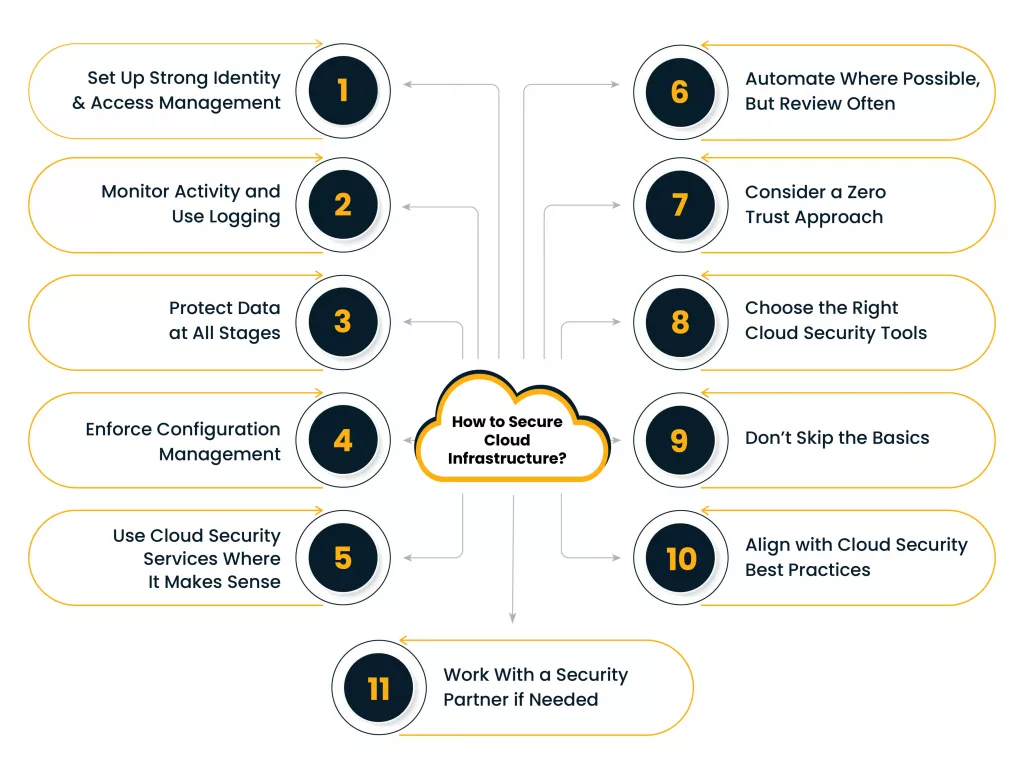
Set Up Strong Identity and Access Management
One of the easiest ways for attackers to get in is through weak user access. That includes simple passwords, shared accounts, or over-permissioned roles.
Use these steps to reduce the risk:
- Require multi-factor authentication for all users
- Don’t give users more access than they need
- Review access rights regularly and remove old accounts
- Use role-based access control for consistent permissions
These actions help reduce your attack surface and limit the damage if an account is ever compromised.
Monitor Activity and Use Logging
Securing cloud infrastructure means knowing what’s happening in real time. Monitoring tools help detect suspicious behavior before it turns into a major problem.
Set up logging across your cloud systems to track:
- Who accessed what data, and when
- Unusual login patterns or failed login attempts
- Changes made to configurations or user roles
- Movement of sensitive files or databases
Logging doesn’t stop attacks, but it helps you find out what happened, how it happened, and what needs fixing.
Many businesses use third-party cloud security tools for real-time monitoring, alerts, and compliance tracking. Choose tools that fit your platform and workload without slowing things down.
Protect Data at All Stages
Data can be at rest (stored), in transit (moving), or in use (being processed). Each stage needs to be secured.
Here’s what you should be doing:
- At Rest: Use encryption on storage buckets, disks, and databases
- In Transit: Use TLS for secure communication between systems
- In Use: Limit who and what can access critical data in real time
Also, make sure data backups are encrypted and tested regularly. If something goes wrong, you need to know you can recover your data safely.
Enforce Configuration Management
Misconfigurations are one of the top causes of cloud-related incidents. These errors happen when security settings are skipped or done incorrectly during setup.
To avoid this:
- Use pre-approved templates or scripts to deploy resources
- Automate configuration checks using security tools
- Avoid manual setup wherever possible
- Run regular scans for exposed ports or open storage buckets
Maintaining good cloud infrastructure security means keeping your setup consistent, repeatable, and easy to check.
Use Cloud Security Services Where It Makes Sense
Most cloud providers offer built-in security services. These are often underused or misconfigured. They can help you:
- Detect threats
- Block suspicious IPs
- Control access
- Enforce compliance settings
Depending on the provider, you might also get identity services, firewall management, key storage, and more.
Using the right cloud security services can fill security gaps and support your team without adding more workload.
Automate Where Possible, But Review Often
Automation helps keep systems consistent and reduces human error. But it also needs oversight. It’s not enough to set something once and assume it works forever.
What to automate:
- Security patching
- Resource provisioning with secure defaults
- Backup scheduling
- Access control policies
What to review:
- Audit logs
- Firewall rules
- User permissions
- Storage settings
Automating key security tasks is helpful, but don’t ignore the need for regular manual reviews. People still need to check the system and make adjustments.
Consider a Zero Trust Approach
Zero Trust means assuming that no part of your system is automatically safe. This model works good in cloud environments where users, devices, and apps are all over the place.
Some Zero Trust steps:
- Validate user identity before granting access
- Use network segmentation to limit movement
- Enforce strong endpoint protection
- Require continuous authentication where possible
This mindset helps strengthen cloud infrastructure security by making sure every request is checked, and every access is earned.
Choose the Right Cloud Security Tools
Choosing the right tools depends on your team, systems, and goals. But at a minimum, most businesses need:
- Threat detection and response platforms
- Identity and access management tools
- Data protection services
- Policy enforcement systems
Look for cloud security tools that integrate well with your cloud provider and fit into your workflows. Some businesses also work with managed service providers to help them choose and configure tools that match their size and security needs.
Don’t Skip the Basics
Some of the most serious breaches happen because of overlooked basics. No matter how advanced your cloud system is, simple mistakes can leave the door open.
Make sure your team:
- Keeps software and operating systems updated
- Disables unused accounts and services
- Uses strong passwords and MFA
- Regularly reviews security policies
These steps are easy to ignore but critical for securing cloud infrastructure in any environment.
Align with Cloud Security Best Practices
Following cloud security best practices helps keep your business aligned with industry standards. This is especially essential for companies working in finance, healthcare, or government.
Recommended frameworks to follow:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- CIS Controls for Cloud
- ISO/IEC 27001
These frameworks help businesses stay compliant and secure, even as cloud systems grow more complex.
Work With a Security Partner if Needed
Cloud security is not always a one-person job. If your business doesn’t have the internal resources, working with outside experts is often the better choice.
Reputable cloud security services can help with:
- Cloud audits
- Compliance assessments
- Security operations
- Incident response
Getting the right help means you don’t have to do everything in-house—and you reduce the risk of overlooking something critical.
Don’t Wait for Trouble—Secure Your Infrastructure Now!
Cloud systems often look fine—until they don’t.
Issues usually show up when it’s too late: a breach, a failed audit, or an outage that costs more than expected. These problems don’t come out of nowhere—they build quietly when security is put off or treated as an afterthought. If your team hasn’t had time to review configurations, tighten access, or test fail-safes, that gap will only grow.
Now is the right time to step in, not after something breaks. Why? Because getting ahead of risks means staying in control—and that starts with securing your cloud infrastructure today.