Today, the vast majority of businesses utilize cloud services for file storage, managing data, running applications, and other tasks. Now, the Cloud is essentially indispensable in business.
However, there is still a misunderstanding between two buzzwords, cloud computing vs cloud engineering. Although the two terms look and sound alike, they differ in their area of focus and approach.
| Concept | Cloud Engineering | Cloud Computing |
| Purpose | Designing, automating, and maintaining cloud infrastructure | Using cloud services from platforms like AWS, Azure, GCP |
| Approach | Building and managing systems behind the scenes | Consuming services already set up by cloud providers |
What Is Cloud Engineering?

Cloud engineering is the work done to create and manage cloud systems. It includes planning how everything should run, automating processes to avoid manual tasks, and making sure the system is secure and can scale. These engineers design and maintain the structure that supports cloud services.
Some of the work includes:
- Designing how cloud environments should be set up
- Automating tasks like deployments and updates
- Keeping an eye on system health and spotting issues early
- Setting up security and user access controls
They often use tools like:
- Terraform or AWS CloudFormation to define infrastructure through code
- Kubernetes to manage containers
- Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI for continuous integration and deployment
- Datadog and Dynatrace for monitoring and alerts
Their goal is to make cloud systems reliable, secure, and easy to maintain, while also keeping costs under control.
The Role of AI in Cloud Engineering
The impact of AI on cloud engineering is becoming more noticeable. AI tools are helping engineers do their jobs more efficiently by detecting problems early and making smarter decisions about resources.
Certain technologies, for example, can ascertain abrupt spikes in server usage. Rather than waiting for someone to detect these changes, systems can self-adjust by
- Scaling up resources
- Returning to a prior version
- Stopping non-essential services
For instance, Dynatrace uses AI to track how applications interact and proactively identify the source of problems and slowdowns.
Some environments deploy reinforcement learning for dynamically predicting workload changes and resource allocation.
According to a hybrid-cloud study, these AI-based provisioning models can reduce cloud spending by 30–40% compared to manual or rule-based scaling.
Cloud engineers now often rely on AI for:
- Making systems run better without needing constant attention
- Automating fixes when something breaks or slows down
- Updating infrastructure in a way that is trackable and repeatable
What Is Cloud Computing?
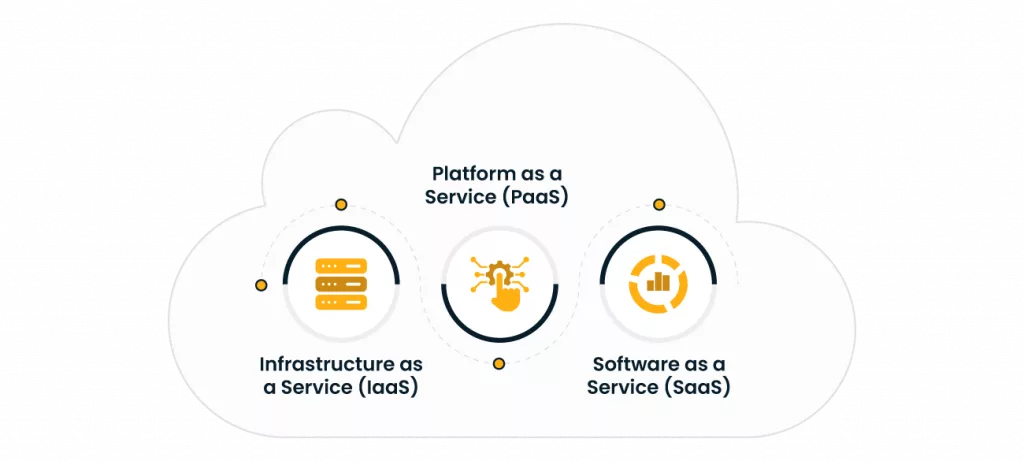
When a company uses third-party services, apps, or infrastructure that have already been developed and managed—like those provided by AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud—it is called cloud computing. Instead of kicking off from zero, businesses simply pay for what they utilize.
There are 3 cardinal cloud computing services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Renting virtual machines or storage (e.g., AWS EC2)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Using a ready-made environment to run code (e.g., Azure App Service)
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Using comprehensive software tools handled by the provider (e.g., Salesforce or Microsoft 365)
Companies rely on these services for tasks like:
- Running websites or online shops
- Handling the following:
- File sharing
- Other day-to-day tools
- Analyzing large data sets without managing physical servers
- Using business software that is available from anywhere
With cloud computing, the provider handles the backend. Businesses just use the tools.
Key Differences
| Category | Cloud Engineering | Cloud Computing |
| Focus | Designing and building infrastructure | Using services built and managed by providers |
| Daily Tasks | Writing infrastructure code, monitoring, scaling | Setting up accounts, configuring tools, running reports |
| Tools Used | Terraform, Kubernetes, Jenkins, Datadog | AWS EC2, Azure Functions, Google BigQuery, Salesforce |
| Who Uses It | DevOps teams, architects, infrastructure engineers | Marketers, business users, analysts, and general IT teams |
| Main Benefit | Custom setups, control, better performance | Speed, simplicity, and less overhead |
Business Use Cases
Let’s break down where each approach fits best.
Cloud engineering is useful when:
- A company is moving complex systems like ERP or databases to the cloud and needs custom infrastructure.
- Development teams work with containers and need automated testing and deployment.
- Compliance standards require custom setups, especially in industries like healthcare or finance.
Cloud computing is ideal when:
- A business wants to launch a website quickly. Plus, it does not want to manage servers.
- Teams need easy access to tools. It can include Slack, Microsoft 365, or Google Workspace.
- Staff need dashboards or reports without worrying about the technical backend.
The difference between cloud engineering vs cloud computing becomes clearer when you look at the problem you are trying to solve.
And the decision is not small. 96% of businesses use at least one public cloud. 50% of businesses run half or more of their workloads there. That means almost every company relies on the cloud, and choosing the right approach has a real impact on results.
Why It Matters to Understand the Difference
Getting this wrong can cost money and time. Some businesses hire cloud engineers when all they needed was a managed service. Others try to stretch basic SaaS tools for complex use cases and end up with limitations or security risks.
According to a report, 94% of companies now use cloud services. But many still do not get the all-inclusive value out of their investment. That’s often because the services they are using do not match what they actually need.
Understanding cloud engineering vs cloud computing helps businesses avoid those mistakes. It gives teams a clearer path to building the right systems with the right tools.
Why Work With Cygnet
Cygnet.one works with companies to plan and execute cloud strategies based on what the business actually needs. Whether it is building infrastructure from the ground up or selecting the right cloud tools, they support each step with deep technical know-how.
What makes Cygnet a solid partner:
- Over 25 years in IT and cloud transformation
- Plausible background in automation, DevOps, and engineering
- Step-by-step consulting that starts small & scales as needed
- Modular services that fit different business sizes and goals
- Ongoing support with AI-based tools for monitoring and stability
- Proven experience managing over 50TB of critical business data
Cygnet helps clients who want full control over their systems and those who prefer ready-to-use services. They help businesses avoid overbuilding or underplanning.
Smart Cloud Decisions Begin with the Right Partner!
Developing a clever IT strategy requires knowing when to use cloud computing and when to use cloud engineering. They have separate functions, thus neither is superior to the other. Companies that are aware of the differences:
- Make smarter decisions
- Maximize their cloud investment
- Steer clear of unpleasant surprises down the road
Cygnet.one can help you take that step with clarity and confidence. Whether you are building or buying cloud services, they bring the right support to make it work.