GST Compliance India: Introduction
Imagine a large enterprise that is always compliant and regular in GST filings, ensuring that it takes ITC only where all relevant conditions including reflection in GSTR 2B is complied with, proactively ensures that ITC of items blocked under GST law is not taken. Even after ensuring that proper compliance, it still receives notice from the GST department as it missed to distribute ITC of common services received at the head office and now potentially faces disallowance of ITC along with interest and penalty liability, not because of any fraud or suppression, but only due to the lack of awareness about the recent mandate on ISD.
The GST law and its compliances have been continuously evolving since its introduction. The evolution has aimed towards a more streamlined and tech-savvy but at the same time enforcing stricter control, institutionalizing accountability, and bringing more structured and transparent compliance.
In 2025, GST compliance is not a routine return filing task but a strategic priority for tax heads and businesses to stay updated continuously to ensure their business operations and systems are aligned with the latest compliance requirements.
While businesses may face many challenges in adopting to the changes, implementing a proactive and robust GST compliance practices, leveraging technology, and of course staying updated, is the way to ensure that the compliance requirements are met and notices, penalties, etc. are avoided.
This blog explores in detail, all mandates and changes either already implemented or in the process of being implemented in the coming months, their impact, challenges, and the practices businesses should follow to ensure GST compliance in India.
GST updates and mandates to be considered in 2025
India’s GST framework is evolving with significant updates and mandates effective in 2025, aimed at enhancing compliance, reducing tax leakages, and streamlining credit distribution. The key mandates and updates are as follows:
Amendments already made applicable
1. Input Service Distributor (ISD)
The Input Service Distributor mechanism was optional since introduction of GST but has been mandatory from 1st April 2025.
Earlier, businesses were either using cross charge mechanism to distribute the ITC services which are used by more than one location or in most cases, no distribution was happening and the ITC was being availed and utilised / reversed at the location where the invoice was received. With ISD being mandatory, ITC for any third-party services received for the common use of all or more than one branch/location or unit shall be distributed through the ISD mechanism.
An input service distributor is an office of a supplier of goods or services that receives tax invoices for the input service, including invoices for the input service charged under RCM for or on behalf of a distinct person (person with a different GSTN registration but the same PAN). This means that every company who has an office (typically head office) which receives invoices for services that are ultimately consumed by a location in a different state, it will have to obtain a separate ISD registration ISD and distribute such ITC and file separate GST returns. For more understanding of ISD, kindly visit our blog “Understanding of Input Service Distributor (ISD) under GST”.
2. Invoice Management System
The GST law, when introduced, envisaged not only filing of outward supply data for each invoice separately i.e. GSTR 1, but the details of ITC availed on the inward supply was expected to be reported in form GSTR 2 and form GSTR 3 was supposed to be the summary of these 2 returns. Owing to technical glitches and the push back from the industry the said process never saw the light of the data and instead a simplified GSTR3B was introduced which only required a summary level reporting of the ITC availed.
In October 2024, the Invoice Management System (IMS) was introduced with a primary objective to achieve transparency in the manner in which ITC is availed by taxpayers at the same time giving more control to the taxpayers in managing their ITC.
The IMS is currently optional given that the GST law, does not contain enabling provisions effective as on date. However, recommendations were made in the 55th Council meeting to update the legal framework related to GSTR-3B, ITC reversal, adjustment of outward tax liability, etc, which were carried in the Budget 2025 and these changes, when observed carefully suggest that IMS may soon become mandatory, once these changes are notified. For a better understanding of IMS, kindly visit our blogs on What IMS is and its key implications.
3. Mandate on Tables 12 and 13 of GSTR-1/1A
Phase-3 of reporting of HSN codes in Table 12 of GSTR-1 & 1A as per Notification No. 78/2020 – Central Tax dated 15th October 2020 has been implemented from the May 2025 return period. Further, table 13 of GSTR-1/1A is also being made mandatory for the taxpayers from the said tax period.
In this phase, manual entry of HSN has been replaced by choosing the correct HSN from the given drop-down. Table 12 has also been bifurcated into two tabs, namely B2B and B2C, to report these supplies separately.
Further, validation regarding values of the supplies and tax amounts involved in the same has also been introduced for both tabs of Table 12. However, in the initial period, these validations were kept in warning mode only, which means that failing the validation will not be a blocked for filing GSTR-1& 1A.
4. Case-insensitive IRN generation
From 1st June 2025, the invoice number shall be treated as case-insensitive in IRP to avoid document duplication and ensure accuracy. This means any alphabets, if used in the invoice number, shall be converted into uppercase before the generation of the IRN. At Cygnet, this has already been implemented to avoid any duplication or other technical issue.
5. Multi-factor authentication
From April 1, 2025, mandatory multi-factor authentication shall be applicable for all taxpayers to access GST portals.
6. E-Invoice Reporting
From 1st April 2025, taxpayers with an Aggregate annual turnover of 10 crores and above must report their e-invoice to IRP within 30 days from the date of the invoice.
7. E-way bill amendments
From 1st January 2025, the e-way bill generation is restricted to a base document which cannot be older than 180 days as on the date of generation of the e-way bill, and the total extension period of the e-way bill shall not be more than 360 days from the date of original e-way bill generation.
Amendments to watch out for
1. Locking of auto-populated liability in GSTR-3B
From the July 2025 tax period, (GSTR 3B to be filed in August 2025), the liability auto-populated in GSTR-3B based on the outward supplies declared in GSTR-1/ GSTR-1A/ IFF, will be non-editable. Thus, in case after filing GSTR 1, if the taxpayers observe any discrepancy in the returns that taxpayers will be allowed to amend their auto-populated liability by making amendments through form GSTR 1A, which can be filed for the same tax period before filing of GSTR 3B.
Based on an earlier advisory, which was later put on hold, it can also be safely assumed that one the IMS is made mandatory, the Government will also lock the ITC in the GSTR 3B on the basis of the GSTR 2B that is generated from the actions taken in IMS.
2. Barring of filing GST Returns for the past periods
Section 39 (11) of the CGST Act, 2017 was inserted w.e.f 1 October 2023 which provided that the taxpayers shall not be allowed to file their GST returns after the expiry of a period of three years from the due date of furnishing the said return. This was not enforced on the portal till now. However, as per Advisory dated 18 June 2025, the said restriction shall be implemented form 1 August 2025 and the taxpayers will not be allowed to file their GST returns where a period of three years has expired from the due date of furnishing the said return. The returns covered are GSTR-1/IFF, GSTR-3B, GSTR-4, GSTR-5, GSTR-6, GSTR-7, GSTR-8, GSTR-9 and 9C.
3. Pending option for Credit Notes in IMS
Since the introduction of IMS in October 2024, pending action was not allowed on certain documents such as Credit notes and their upward amendments and downward amendments to invoices and debit notes. This was causing a lot of difficulties for the industry given that the rejection of these documents resulted in adding back of such values to the liability of the supplier.
To resolve this, the Government is planning to introduce the ability to mark these documents as pending. As per the API release Notes dated 13 June 2025, effective from the July 2025 period, the Pending option shall be made available in IMS for 1 tax period for the following documents:
- Credit Notes
- Amendments to Credit Notes (except for downward amendment of CN) where original CN is accepted
- Downward amendments to B2B Invoices, Debit notes, and ECO-documents where the original B2B invoice/debit note/ECO document, respectively, is accepted.
While the ability to mark these documents for a only 1 months is something that is not exactly what was required by the industry, it certainly will provide a big relief for the industry. The recipients will have reasonable time in hand to communicate with the vendors and resolve issues before taking reject or accept actions.
Strategies for effective GST Compliances beyond return filing
While filing timely returns is vital for businesses, it is only a part of the entire compliance process for tax heads in 2025. Businesses are required to adapt to the ever-evolving GST law, the compliances therein, must stay updated with all amendments and mandates, and comply with them to avoid notices and penalties, vendor / supplier discrepancies affecting supply chain.
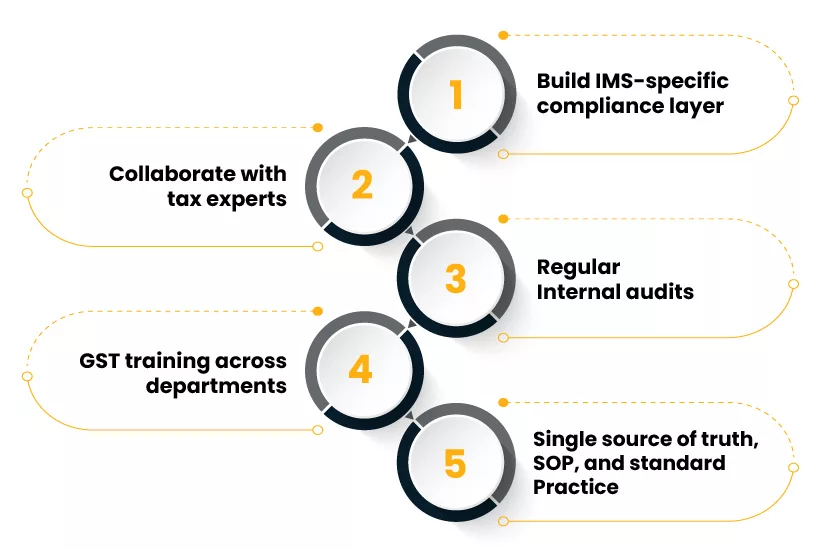
Here are some of the practices a business may follow to stay updated and complaint with the requirements of GST.
Build IMS-specific compliance layer
The IMS will eventually become mandatory – the question is not if, the question is only when. When that happens, businesses who had not taken IMS seriously may suddenly have to undergo a shift in business processes which may lead to a chaos. As of today as well, though IMS is not mandatory, it is vital to ensure that atleast pending and reject actions are taken in IMS to ensure real-time validation and correct flow of ITC in GSTR-2B and later in GSTR-3B.
As, as stated above, the locking of outward liability in GSTR 3B is already mandated in the coming months. Once, IMS is made mandatory, the next step will be to freeze the ITC in GSTR 3B from the GSTR 2B generated on the basis of IMS actions which makes IMS an aspect of business which cannot be ignored at any cost.
Collaborate with tax experts
Businesses must partner with tax experts or have an internal team of tax experts to get regular updates on amendments and mandates, along with correct interpretations and advice on whether a particular amendment is applicable to them or not, to avoid confusion and non-compliance.
Regular Internal audits
Conduct internal audits on a regular basis, scheduled quarterly or semi-annually based on the size of the business and volume of transactions, covering all regular compliance audits as well as a review of compliance with amendments.
Prepare a structured checklist aligned with GST regulations and amendments applicable to the business. Analyze all the findings, correct the errors, and maintain detailed records of the audit with evidence for future notices and government audits.
GST training across departments
Ensure GST trainings and webinars are organized at regular intervals for employees across departments to equip them to handle GST requirements, amendments, and mandates. Circulate internal mails and newsletters on the latest trends, amendments, etc, to ensure cross-department awareness.
Single source of truth, SOP, and standard Practice
A single source of truth with standard operating procedures ensures consistency and compliance in the workflow process. There should be an integrated GST solution for all compliance requirements, such as e-invoicing, e-way bill generation, IMS implementation, return filing, reconciliations, notice management, etc, integrated with the ERP system. Develop detailed SOPs for key GST and notice management process, specifying steps, responsibilities, and timelines. Standardize practices across locations and departments, ensure uniformity, minimize errors, and simplify compliance management.
How is Cygnet your one-stop solution for GST compliance requirements?
Cygnet offers a comprehensive suite of tech-driven solutions to streamline the GST compliance process for all business sizes, ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and adherence to the GST compliance in India.
Cygnet’s platform automates critical processes such as GST return preparation and filing, e-invoicing, e-way bill generation, IMS implementation, ISD compliance, etc, reducing manual intervention and errors. With AI-ML-driven tools, Cygnet facilitates up to 99% compliance through features like automated 6-way reconciliations, real-time validation, and vendor invoice reconciliation to optimize ITC availment.
Cygnet’s platform seamlessly integrates with over 200 ERP systems, including SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft, enabling businesses to manage high transaction volumes while maintaining data privacy through robust security measures, certifications, and encryption algorithms.
Further, Cygnet also facilitates specific compliance challenges through modules like notice management, which retrieves GSTN portal notices and auto-drafts responses. It also uses AI to identify issues per tax laws, ensuring timely and error-free handling. Cygnet ensures risk mitigation and time savings, achieves audit readiness for businesses, and helps them stay compliant with the continuously evolving GST law.
Conclusion
With GST completing 8 years in 2025, Indian business must now focus on mastering GST compliance to manage the changing tax system, steer clear of penalties and run their operations. Businesses can reduce risks and handle compliance better through strategic practices and the integration of advanced technology.
Using advanced tools such as Cygnet’s platform, powered by AI and ML, helps automate key tasks, improve data accuracy, and offer helpful insights for decision-making. These efforts not only protect financial stability but also build trust with stakeholders and set the foundation to grow within India’s fast-paced GST framework.